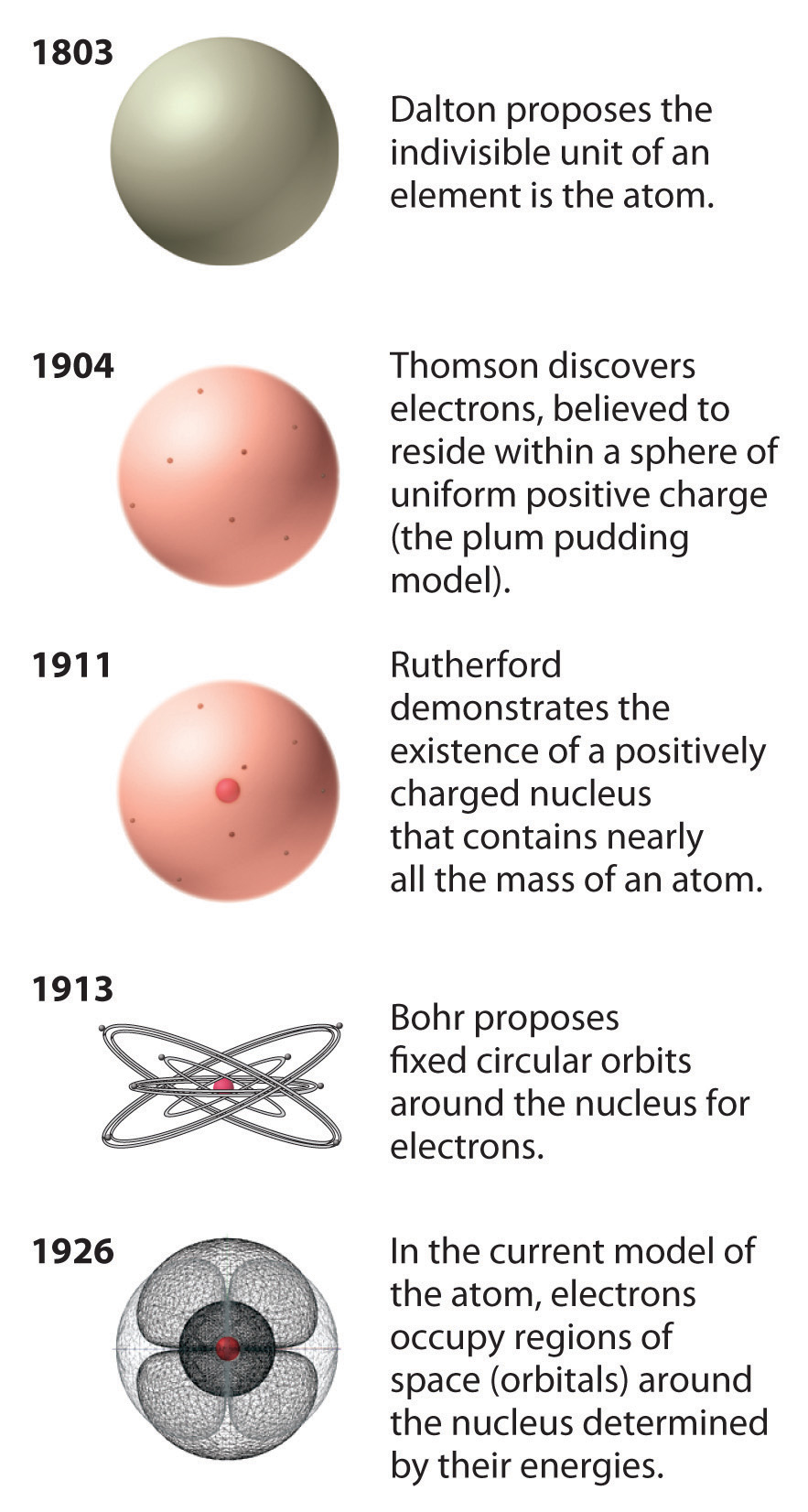
Chapter 1.5 The Atom Chemistry LibreTexts
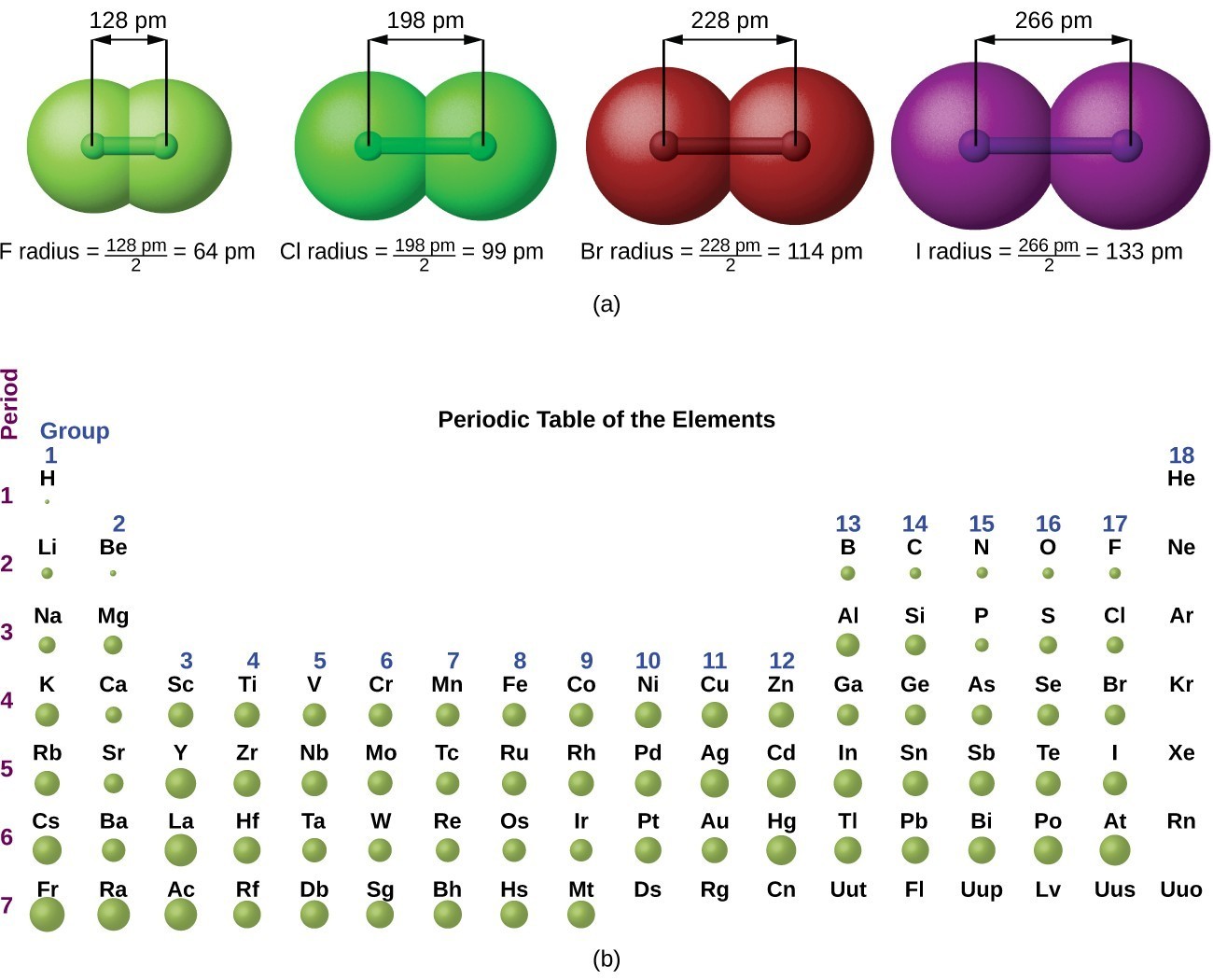
Atomic radii are often measured in angstroms (Å), a non-SI unit: 1 Å = 1 × 10−10 m = 100 pm. Figure 7.3.2 7.3. 2: Definitions of the Atomic Radius. (a) The covalent atomic radius, rcov, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule, such as Cl 2.

(Color online) Proposed mechanism (a) creation of atomic species, (b
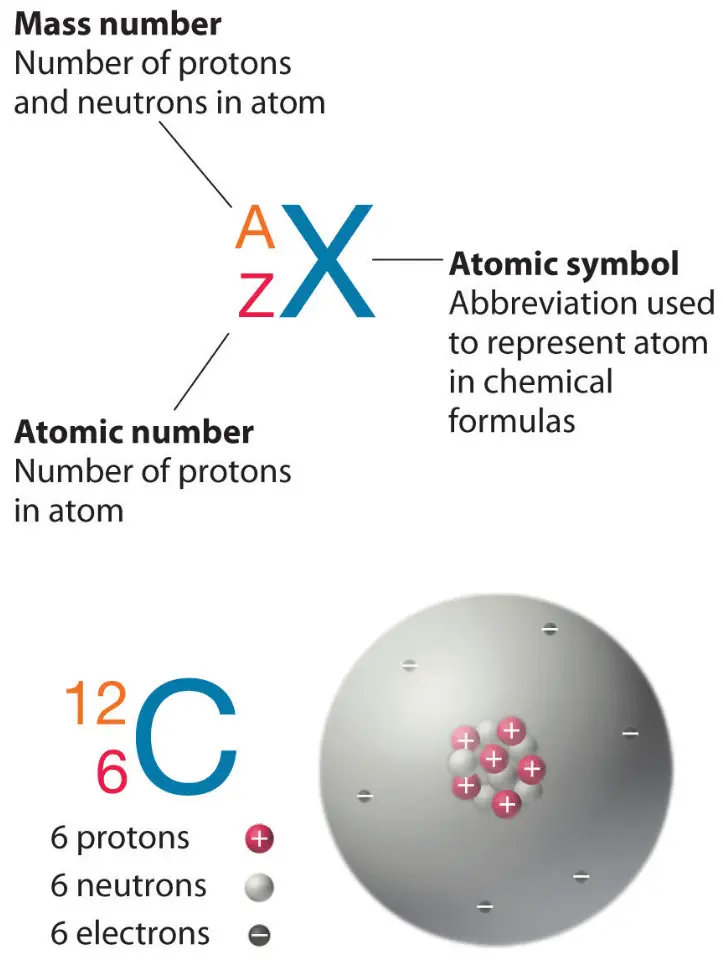
The total mass of neutrons, protons, and electrons found in an atom determines its mass number or atomic number. There are several atomic species centred on this. They are known as isotopes, isotones, isobars, and isoelectronic.
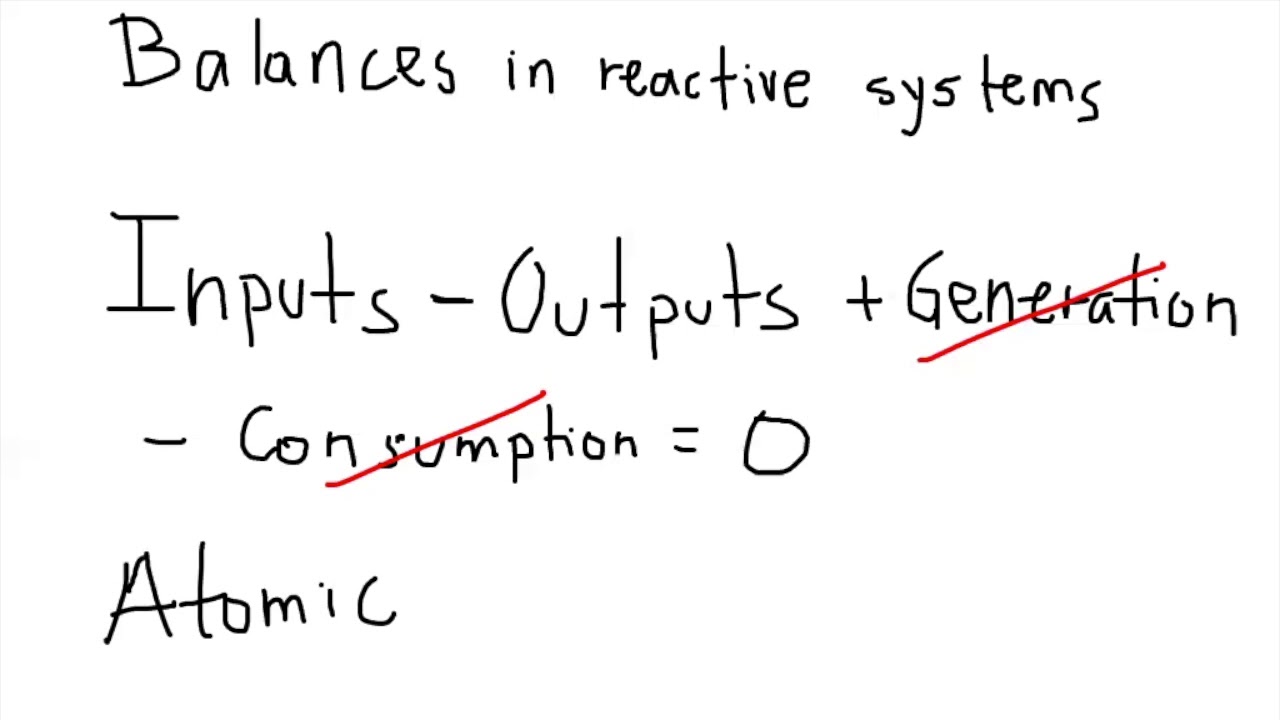
3.2 Balance for atomic species YouTube
ulated with conventional atom optics (e.g. two-photon Raman transitions [28]) in order for the paths of each species to interfere. Single atom detectors are nally used to probe the atomic interference at the interferometer output. We focus in this letter on a particular implementa-tion of this idea using 85Rb and 87Rb atoms, as sketched in Fig.1.

Periodic table of the elements, showing the atomic species in which
The atomic number or mass number of an atom is based on the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons present in them. Based on this, there are different atomic species (isotopes, isobars, isotones, isoelectronic). Atomic Number and Mass Number The number of protons in an atom represents its atomic number. It is denoted by the letter Z.

The AOs 2 O 6 lattice. The atomic species are maker Download
In comparison with the experimental atomic model, all the atom species were correctly identified and the RMSDs of the S, Re and Mo atoms were 18 pm, 3 pm and 3 pm, respectively. Compared with the.

Atomic Species YouTube
First of all, identify the given species whether an atom or ion or molecule. If given species is an atom, its total number of electrons is equal to its atomic number. For example, Argon(Ar) atom has atomic number 18 and a total electron of 18. If the given species is a positively charged ion, then the total number of electron=Atomic number.
PPT Laser Cooling and Trapping of Atom PowerPoint Presentation, free
27 Altmetric Metrics Abstract Anatase is a pivotal material in devices for energy-harvesting applications and catalysis. Methods for the accurate characterization of this reducible oxide at the.

Structure Of Atom 01 Atomic Number , Atomic Mass and Atomic Species
21 First, I would like to quote sentences from a book introducing elements and atoms: An element is a fundamental (pure) form of matter that cannot be broken down to a simpler form. Elements are made up of particles called atoms. An atom is the smallest unit of any element [.]

SOLVEDIn βdecay, an electron comes out from an atom. The electron
A chemical species is a chemical substance or ensemble composed of chemically identical molecular entities. The set of these entities can explore the same set of molecular energy levels on a characteristic or delineated time scale.

Class 11th Chemistry Structure of Atom Complete Notes for IIT JEE
Fractional Conversion (Interactive) Limiting Reagent (Interactive) Reaction Stoichiometry (Interactive) Three Methods for Reactive MEB Problems. Atomic Species Balances. Extent of Reaction for Material Balances. Molecular Species Balances. Two Reactions in a Two-Phase Reactor. Percent Excess Air.

Best of Last Week Creating Rydberg polarons, Tesla carrying bacteria
An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter that forms a chemical element. Atoms are made of fundamental particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons clump together to form a central nucleus. The electrons move in a cloud-like region around the nucleus. Most atoms are stable.
Iridium Protons Neutrons Electrons Electron Configuration
Abstract. The capability to reach ultracold atomic temperatures in compact instruments has recently been extended into space 1, 2. Ultracold temperatures amplify quantum effects, whereas free fall.
Periodic Variations in Element Properties General Chemistry
Figure 8.2.2 8.2. 2: Definitions of the Atomic Radius. (a) The covalent atomic radius, rcov, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule, such as Cl 2. (b) The metallic atomic radius, rmet, is half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a pure solid metal, such as.

Bohr's Model for Hydrogen Atom Postulates, Merits, Limitations
Here we report the precise determination of the 3D coordinates and chemical species of 23,196 atoms in a single 8.4-nm Fe 0.28 Pt 0.72 nanoparticle using atomic electron tomography (AET) 1. FePt.
FileSchematicky atom.png Wikimedia Commons
The APFIM provided essentially a one-dimensional series of atomic species as the sample was 'eroded' one atomic layer at a time. Continued improvements and new configurations of the hardware through to the mid-1990s resulted in position-sensitive ion detection, in combination with full-spectrum time-of-flight mass spectrometry (Cerezo et al.

4 nm thick sections from atom maps showing distribution of atomic
The simplest conceivable molecule would be made of two protons and one electron, namely \ (\ce {H2^ {+}}\). This species actually has a transient existence in electrical discharges through hydrogen gas and has been detected by mass spectrometry and it also has been detected in outer space. The Schrödinger equation for \ (\ce {H2^ {+}}\) can be.